Role of air domain size
For every simulation you create, an air domain or simulation environment is a necessity. It is not only needed for the electromagnetic calculations, but its size can have a strong impact on the simulation results for both workpiece and inductor.
How big the air domain should be?
Air domain around the geometry can be created at different sizes - too small will result in inaccurate results, but too large will increase the element count and through it the calculation time.
The Infinity BC is used for the air domain outer boundaries, meaning that on these surfaces magnetic vector potential is zero. For this condition to be applicable, it is necessary to ensure that electromagnetic field is declining to negligible values at the outer boundary. to satisfy this condition, air domain should be at least 3 times larger than the coil within it.
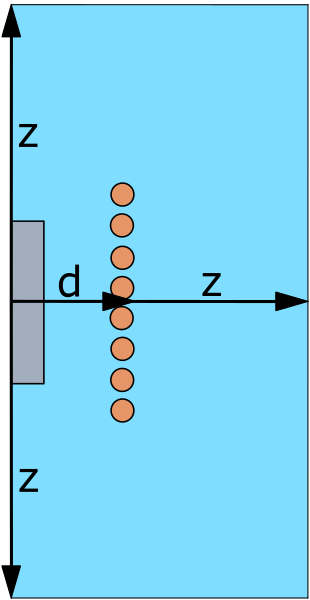
IMPORTANT: If the mesh is too large, the element reduction can be done on the air domain and its size can be reduced to 2.5 times the coil size, but no less! The air domain size is defined as the distance from the center of the coil to the air outer boundary (Z). The coil size is defined with its outer diameter (d).
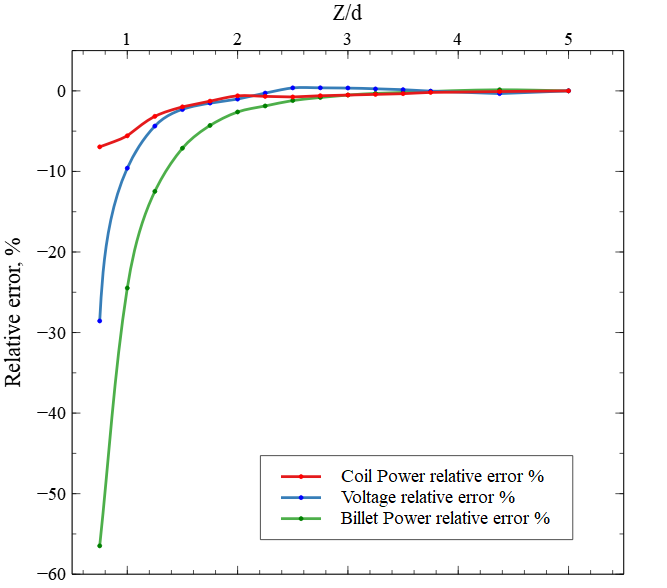
The air domain size is characterized in respect to the coil diameter - if it is more than 3 times the size of the coil diameter, the relative error for voltage, coil and billet is negligible.